Now, mask factories in European and American countries are facing some pressure: on the one…
The Traps of Mask Production: The Most Critical and Latent
In any industry, the more experience and resources you have, the more successful you will be. If you have few resources or little experience, there is a high probability that you will fail. During the 2019-nCoV, we didn’t have enough time to learn and gain experience in this particular industry of face masks, and if we were just trying to figure it out on our own, the market might have been oversaturated before we were successful.
If you’re in the business to produce a competent mask, it’s best to learn from others’ experiences to avoid getting into the trap of mask production, so that you can cut corners and accomplish your goals efficiently. Here I share with you the most critical and the hardest to detect traps in the mask manufacturing process.
Table of Contents
- Trap #1 of mask production: experience in purchasing mask raw materials
- 1 Meltblown fabric filter efficiency can not be judged by the feeling, not by the naked eye, must be tested.
- 2 The relationship between filtration efficiency and respiratory resistance of meltblown fabric
- 3 Effect of the size of meltblown and spunbond nonwovens on respiratory resistance
- 4 Packaging, storage, and transport of nonwovens
- 5 Suppliers to have their own standards for raw materials for masks
- 6 Do not attempt to produce meltblown fabric
- Trap #2 of manufacturing masks: experience in purchasing mask making machine
Trap #1 of mask production: experience in purchasing mask raw materials
There are four kinds of raw materials involved in mask production: meltblown nonwoven fabric, spunbond non-woven fabric, nose bridge wires, and earloops. The most important and most expensive material is meltblown nonwoven fabric. If you are worried about purchasing the raw materials of masks and don’t know how to make a decision, the following experiences will surely help you.
1 Meltblown fabric filter efficiency can not be judged by the feeling, not by the naked eye, must be tested.

The filtration efficiency of meltblown cloth usually occurs in two cases, one is not up to standard, one is up to standard, but soon after, the filtration efficiency will be rapidly reduced. There is no instrument to detect, only by feeling, or there is a test, but not the right test, these are the key reasons for buying substandard meltblown fabric.
It’s certainly better if you have your own testing equipment and you know how to do it properly, but what if you don’t? We should look for well-known companies that have there own quality standards, a laboratory, quality control processes and capabilities, formal packaging, and labeling specifications, etc. Because of their years of experience, we don’t have to worry at all about the damage that can be caused by having something we don’t understand. And some suppliers, because they do not understand, may not even know whether their products are up to standard, so the price is very low, easy to attract others to buy more, but actually buy more losses.
2 The relationship between filtration efficiency and respiratory resistance of meltblown fabric
The filtration efficiency of the meltblown cloth and respiratory resistance is usually directly proportional to the relationship, the higher the filtration efficiency, the higher the respiratory resistance, the more difficult to breathe, which can easily cause lung damage. Therefore, in the purchase of meltblown cloth, we can not only pursue the standard of filtration efficiency but also test the permeability of meltblown cloth.

3 Effect of the size of meltblown and spunbond nonwovens on respiratory resistance
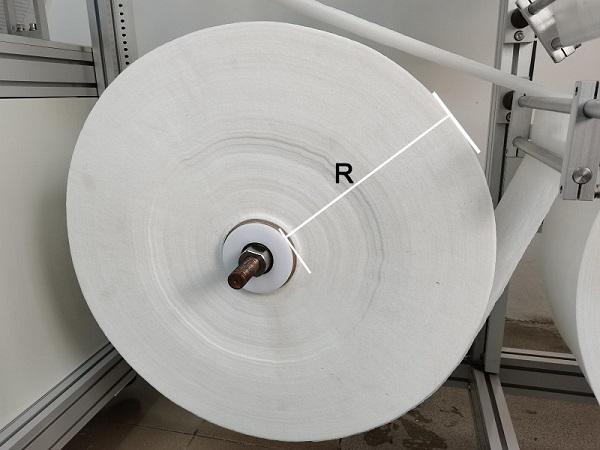

During the mask manufacturing process, we found that when R is too large, the inner layer of the non-woven fabric is under too much pressure, and the fabric is subjected to pressure for a long period of time resulting in poor breathability, which can lead to greater respiratory resistance of the mask. If the R is too small, it can lead to excessive fabric tension, resulting in an unstable mask size and the need for frequent, time-consuming fabric changes. Therefore a reasonable R is also a key factor in the stable mass production of qualified masks.
4 Packaging, storage, and transport of nonwovens
Packaging: Product packaging materials should ensure that product quality is not damaged, easy to transport.
Transportation: The products should be protected from light, water, moisture, pollution, breakage and extrusion during transportation.
Storage: The products should be stored in a dry, ventilated, light-proof and clean environment, away from fire and flammable materials.
5 Suppliers to have their own standards for raw materials for masks
If there is no uniform standard for the raw material of the mask, Some non-woven fabrics are thicker, some are thinner, some nose bridge strips are thicker, some are thinner, some earloops are looser, some are tighter… The mask produced in this way may cause the size of the mask to vary, the length of the earloops straps, etc., which will result in waste of material and the production of substandard masks.
Corporate standard of earloop: Check the TESTEX mask earloop standard (Download as Pdf):
Corporate standard of meltblown fabric: Testex Meltblown Standard (Download as Pdf)
Corporate standard of nose wire: Download the metal nose wire standard PDF
Corporate standard of PP-Nonwoven: Download TESTEX PP-Nonwoven Quality Standard
Only by regulating the standard of raw materials for masks can we ensure maximum stability in the quality of masks and produce qualified masks. In addition, the uniform specification of raw materials reduces the difficulty of commissioning the mask making machine.
6 Do not attempt to produce meltblown fabric
The production of meltblown cloth involves high machine and material costs, and the production process is quite complex. For example, for the meltblown cloth 99 production line, the equipment to produce a single layer of meltblown cloth is $400,000, and the three-layer is $1 million. If you invest in a meltblown cloth production line, it will take at least half a month from order to installation and production, and if you are not skilled in the process. It may take 3-5 months.
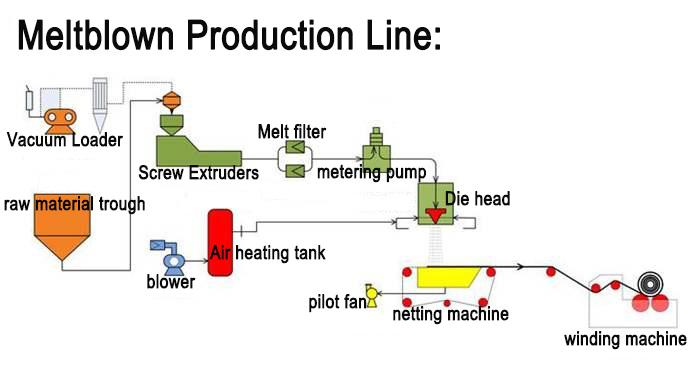
If you don’t have sufficient human and material resources, my advice is not to produce meltblown cloth, as it is not a good investment from a risk-return perspective.
Trap #2 of manufacturing masks: experience in purchasing mask making machine
In addition to the mask raw materials, the most important is the mask making machine, these two are the key to the ability to produce qualified masks, personnel can learn, methods can learn, the environment can be changed, but if the raw materials and mask making machine is wrong, it will cause uncorrectable losses.
1 It doesn’t matter if a video or picture sent, it’s better to have a video link to see what the seller is actually producing!
Due to soaring demand and a lack of supply in the market, many companies that do machining and electronic components began to switch to manufacturing mask machines, but Most factories do not have R&D and mechatronics capabilities, and no more than 15% of the masks made on the market today can run consistently and reliably. A video link or field trip is recommended to be reliable for a mouthpiece machine that can run properly for at least a day.
2 Buy the right mask making machine according to your personnel’s experience
From the degree of automation of the mask making machine, there are mainly three kinds of semi-automatic mask machine, automatic mask machine, fully automatic mask machine. The higher the degree of automation, the more difficult it is to debug, if there is no professional debugger, it is best to buy easy to debug the semi-automatic mask making machine or the main body machine and ear band welding machine separate automatic mask making machine.
| Model | Semi-automatic mask making machine | Automatic mask making machine | Fully automatic mask making machine |
| Output | Theoretical: 90~110pcs/min
Actual: 80~90pcs/min |
Theoretical: 90~110pcs/min
Actual: 80~90pcs/min |
Theoretical: 120pcs/min
Actual: 80~90pcs/min |
| Debugging | Little debug difficulty, stable operation | Little debug difficulty, stable operation | Debug difficult, Harder to stabilize operation |
| Remarks | Requires dozens of people to weld the earloops, produces about 150,000 in 24H. | Requires 2 man operation produces about 100,000 in 24H. | Requires 1 man operation produces about 100,000 in 24H. |
| Pictures |  |
 |
 |
3 Choose a manufacturer with export experience and perfect after-sales service.
The production base of the mask making machine is in Dongguan, China, with few export manufacturers and even fewer manufacturers with perfect after-sales systems. During the epidemic, it was not possible to send after-sales personnel for installation and training, nor could buyers come to China for training. In addition, the export of mask making machines involves packaging materials, the production of export documents, logistics and customs clearance arrangements, the slightest carelessness can be Customs detaining for inspection is as little as 10 days and as much as 30 days.
Choose a manufacturer with export experience and a perfect remote after-sales service system so that the machine can be delivered to the customer safely and quickly to ensure that the customer can quickly master the commissioning and use of the machine and rapid production. “TESTEX” is a national high and new technology enterprise with experience in research and development of automation products, with ten years of experience in import and export trade and Perfect after-sales service system, 90% of the instruments are sold to Europe, America, and Asian countries. The customers are NASA, the Navy, the United States of America. It is also used in national laboratories and university research institutes such as the Research Institute of China (RIC), and international authoritative testing agencies such as ITS, SGS, etc. You can take a comparative look at these areas.





This Post Has 0 Comments